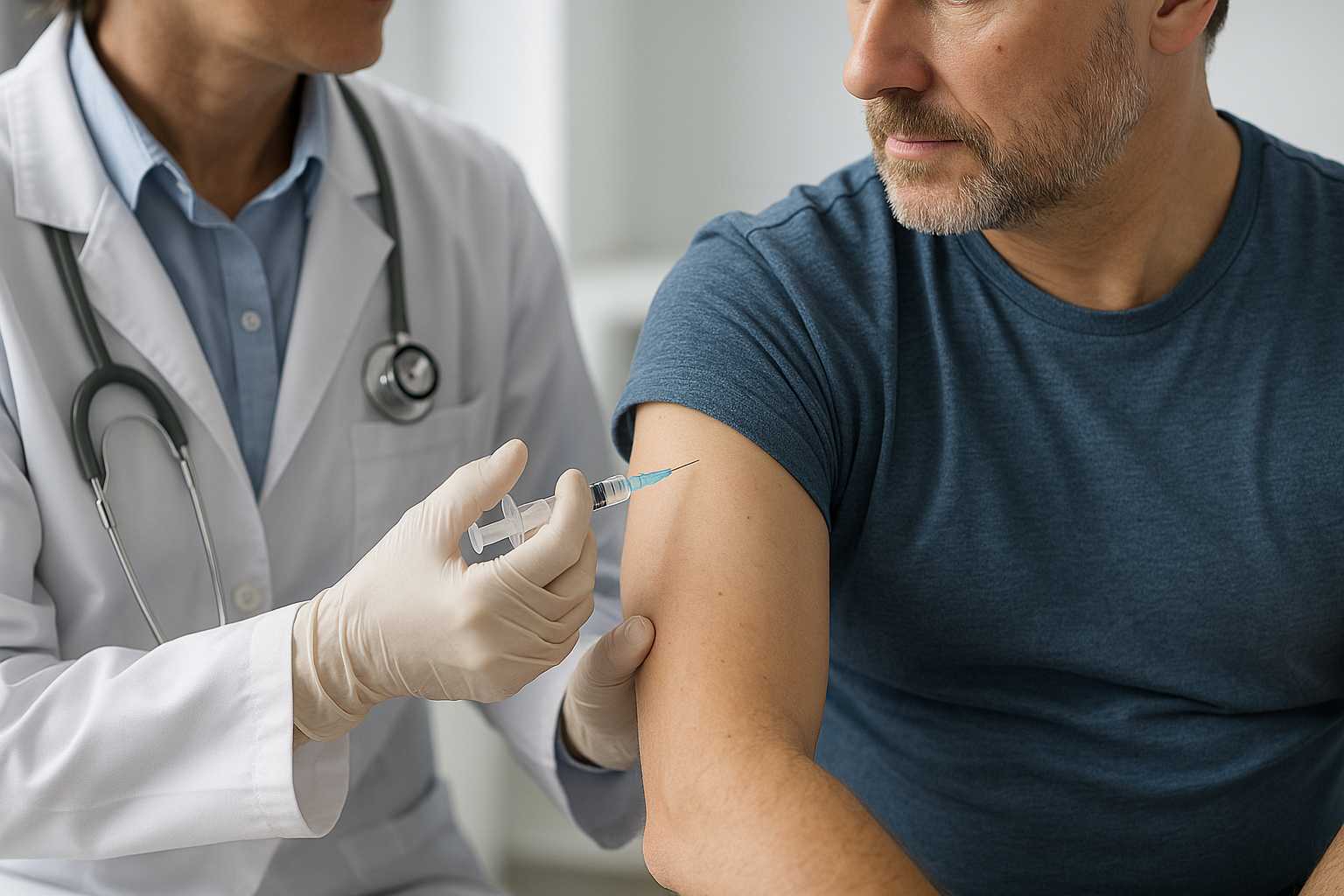
Explore the future of HIV treatment with long-acting injections, new therapies, and innovations that could change how HIV is managed.

Explore the future of HIV treatment with long-acting injections, new therapies, and innovations that could change how HIV is managed.

Learn how PrEP helps prevent HIV, who should consider it, and why it’s a game-changer in global HIV prevention efforts.

Discover how celebrities talking about HIV help fight stigma, raise awareness, and support global prevention and treatment efforts.

Discover how long it takes for HIV to turn into AIDS, the factors that influence progression, and how treatment can change the timeline.

Explore the latest HIV statistics worldwide, uncovering trends, regional impacts, and what they mean for prevention and care.

Discover how long HIV can remain undetected, why early testing matters, and what symptoms to watch for. Learn when and how to get tested.

Learn how HIV prevention medications like PrEP and PEP work, who should use them, and how they reduce HIV transmission risk.

Learn when and where you are legally required to disclose your HIV status and what rights protect you.

Discover powerful, inspirational HIV stories of survival, advocacy, and hope—from cured cases to courageous activists.
Discover how people are surviving HIV today through treatment, mindset, and support. Learn key strategies for living a full life with HIV.
© 2025 Aids.org